Building AI Agents - A Practical Architecture Guide
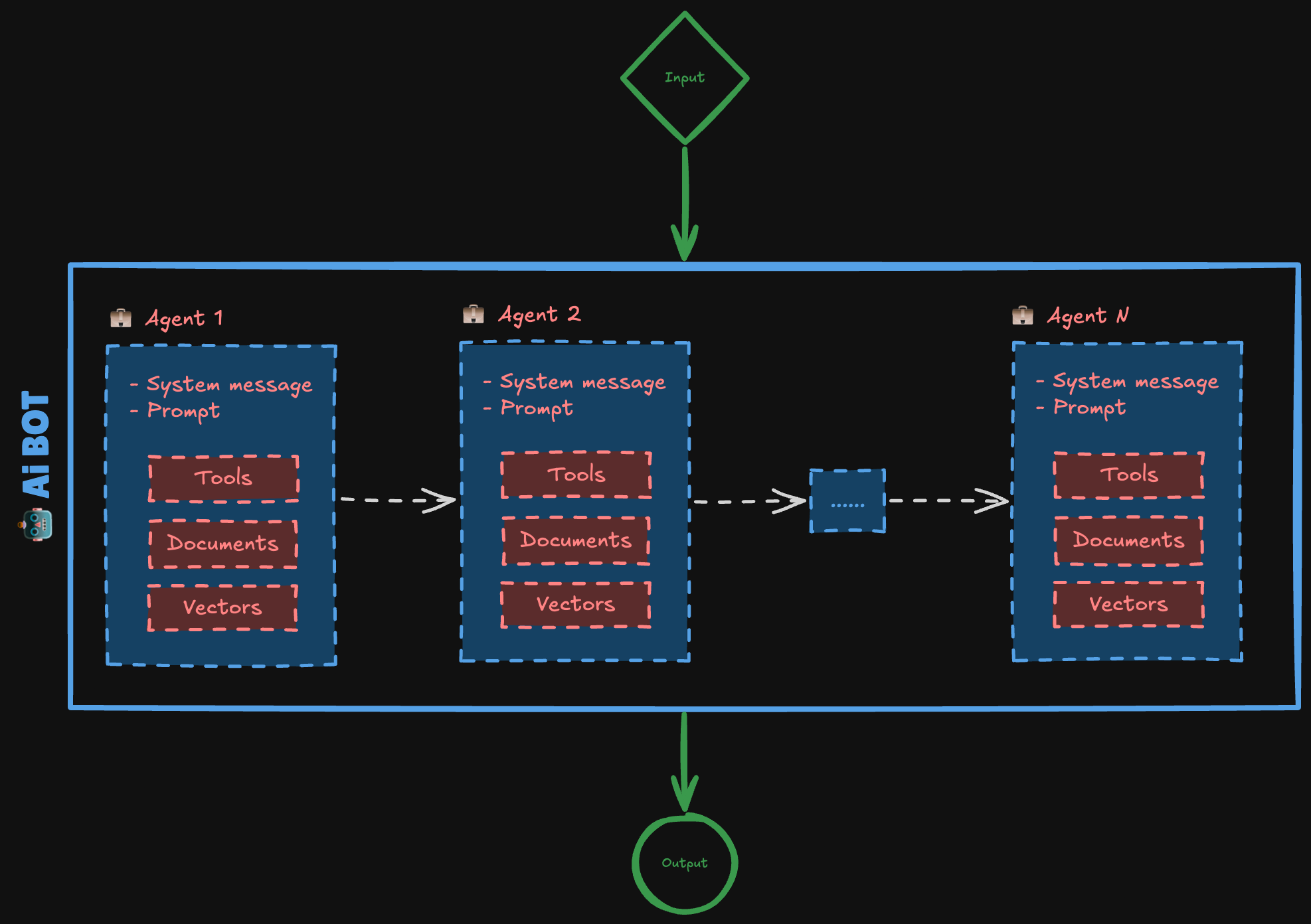
As AI technology evolves, we’re seeing a shift from single-model systems to more sophisticated multi-agent architectures. These systems combine multiple specialized AI agents to handle complex tasks more effectively. Let’s explore how to build such a system and understand its key components.
Core Components
1. Input Layer
The input layer serves as the entry point for user interactions:
- Processes incoming requests and queries
- Handles initial message formatting
- Routes requests to appropriate agents
2. AI Bot (Central Controller)
The AI Bot acts as an orchestrator:
- Manages workflow between agents
- Maintains conversation context
- Coordinates agent responses
- Ensures coherent output generation
3. Specialized Agents
Each agent is designed for specific tasks:
- Agent 1: Could handle document analysis
- Agent 2: Might focus on data processing
- Agent N: Additional agents for other specialized tasks
Each agent contains:
- System prompts defining their role
- Access to relevant tools
- Domain-specific knowledge
- Specialized capabilities
How Data Flows Through the System
User Input → Input Processing
- Query enters the system
- Initial processing and formatting occurs
Input Processing → AI Bot
- AI Bot analyzes the request
- Determines which agents to involve
AI Bot → Agents
- Routes tasks to appropriate agents
- Manages parallel processing when needed
- Coordinates between multiple agents
Agents → AI Bot
- Process their specialized tasks
- Return results to the AI Bot
AI Bot → Output
- Combines agent responses
- Formats final output
- Ensures response coherence
Implementation Tips
Setting Up the Infrastructure
1 | class AIBot: |
Agent Configuration
1 | class Agent: |
Best Practices
Agent Design
- Keep agents focused on specific tasks
- Provide clear role definitions
- Implement proper error handling
System Messages
- Write clear, specific instructions
- Define boundaries between agents
- Include example interactions
Tool Integration
- Make tools easily accessible to agents
- Implement proper authentication
- Monitor tool usage and performance
Error Handling
- Implement fallback mechanisms
- Log errors for analysis
- Provide graceful degradation
Common Challenges and Solutions
Agent Coordination
- Challenge: Agents working at cross purposes
- Solution: Implement clear hierarchies and communication protocols
Resource Management
- Challenge: Efficient resource allocation
- Solution: Implement queuing and load balancing
Response Consistency
- Challenge: Maintaining consistent output quality
- Solution: Implement validation and quality checks
Conclusion
Building a multi-agent AI system requires careful planning and architecture design. The key is to maintain clear boundaries between components while ensuring smooth information flow. By following these patterns and best practices, you can create robust and scalable AI agent systems that effectively handle complex tasks.
Remember that this architecture is flexible - you can add or remove agents as needed, and adjust the system based on your specific requirements. The goal is to create a system that’s both powerful and maintainable.